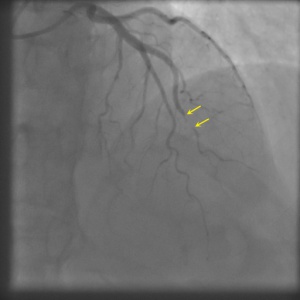
Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection
SCAD Microchapters
Overview
Historical Perspective
Classification
Pathophysiology
Causes
Differential Diagnosis
Epidemiology and Demographics
Risk Factors
Screening
Natural History, Complications and Prognosis
Diagnosis
- Diagnostic Approach
- History and Symptoms
- Physical Examination
- Laboratory Findings
- Electrocardiogram
- Angiography
- CT
- MRI
- Echocardiography
- Other Imaging Findings
Treatment
- Treatment Approach
- Medical Therapy
- Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
- Surgery
- Primary Prevention
- Secondary Prevention
- Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy
- Future or Investigational Therapies
SCAD Angiography
Shown below are animated and static angiography images exemplifying each type of SCAD. For additional angiographic images of SCAD, click here.
Type 1
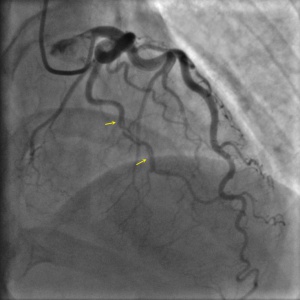
Projection angle: 14 RAO, 35 CRA. Type 1 SCAD is seen in OM2.
Type 2A
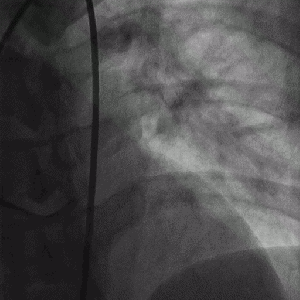
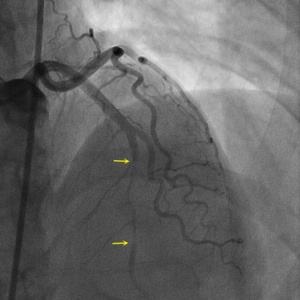
Projection angle: 5 LAO, 34 CRA. Type 2A SCAD is seen in L3.
Type 2B
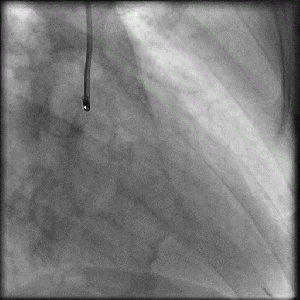
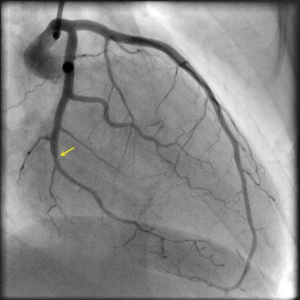
Projection angle: 30 RAO, 1 CRA. Type 2B SCAD is seen in OM2.